With fast changes in the business environment, leadership skills have turned out to be very important. Since organizations are facing constant changes in technology, market dynamics, and customer needs, the concept of a business leader has considerably changed. As a result, leaders should continually update their skills and refine their capabilities with each new challenge that comes before them.
Power skills
Power skills are also known as interpersonal or soft skills, including communication, problem-solving and collaborative leadership. These have become crucial for project professionals. They are at the core of leading successful teams, engaging stakeholders and conquering challenges to the project plan. While technical skills allow a project manager to navigate from the very beginning all the way to the close of a project, power skills are how he or she takes the entire team on that journey.
According to Project Management Institute, power skills are the abilities and behaviors that enable people to work with others – they are what set project professionals up for success in the workplace. Many experts refer to them as “soft skills” or “interpersonal skills.”
Calling these abilities and behaviors “power skills” puts a name to the value they bring to project professionals, teams and organizations. This makes power skills critical in any professional's toolkit.
Individual power skills ranked per region and industry by 2023 PMI Survey respondents:
Most Critical Power Skills by Region
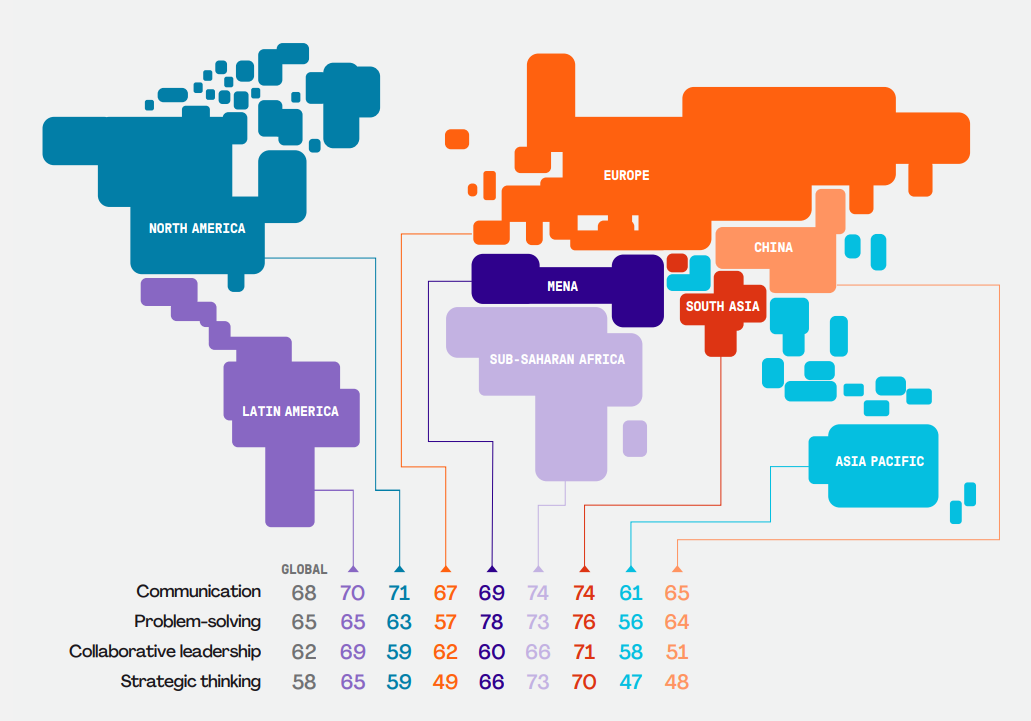
Most Critical Power Skills by Industry
| Skills | Global | Gov't | IT | Financial Services | Telecom | Energy | Manufacturing | Healthcare | Construction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Communication | 68 | 71 | 69 | 64 | 72 | 66 | 66 | 69 | 70 |
| Problem-solving | 65 | 65 | 63 | 62 | 63 | 67 | 68 | 63 | 69 |
| Collaborative leadership | 62 | 64 | 61 | 62 | 66 | 64 | 58 | 60 | 55 |
| Strategic thinking | 58 | 57 | 56 | 56 | 59 | 56 | 57 | 61 | 61 |
| Relationship building | 49 | 49 | 48 | 47 | 47 | 49 | 44 | 48 | 48 |
| Adaptability | 48 | 50 | 44 | 46 | 48 | 50 | 45 | 48 | 51 |
Skill 1: Communication
“The single biggest problem in communication is the illusion that it has taken place.”
― William H. Whyte, American sociologist
Importance of Effective Communication
Clear and effective communication is the foundation of successful leadership skills set. It fosters collaboration, builds trust and drives team success. When leaders communicate well, they can articulate their vision, motivate their teams and resolve conflicts efficiently.
The Impact of Communications Methods on Team’s
Productivity and Performance – Oil and Gas case study
In March 2020, the Technium Social Sciences Journal published a case study about national oil and gas company in Yemen. The whole point of the research? To find out how their teams were communicating and figure out exactly where things were getting messy.
Here’s the kicker – their findings weren’t exactly rocket science, but they nailed why the basics matter. Teams that actually talked to each other with real face-to-face meetings instead of endless emails or messages, simply outperformed the rest.
The study showed that in high pressure industries like oil and gas, where a single miscommunication can cost millions, live conversations aren’t just nice-to-have – they’re the glue holding everything together. Teams with real human interactions had smoother workflows and clearer priorities.
You can read the whole research in ResearchGate.
Improving Your Communication Skills
Active Listening Techniques: Interact with your team through active listening. That is, not just hearing the words of your team members but understanding their feelings and intentions.
Clarity and Conciseness: Be straightforward with what you want to say. Avoid using jargon and say what is necessary so that the message gets across.
Non-Verbal Communication Cues: Be mindful of your body language, eye contact, and tone of voice, as these can significantly impact how your message is received.
Skill 2: Strategic Thinking
“In a world that's changing really quickly, the only strategy that is guaranteed to fail is not taking risks.”
― Mark Zuckerberg, CEO of Facebook/Meta
Understanding Strategic Thinking
Strategic thinking is the ability to analyze complex situations and make decisions based on long-term business objectives. Leaders should be able to anticipate challenges and opportunities in the marketplace.

Developing Strategic Thinking
SWOT: Rethinks an organization's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats on a periodic basis to ensure informed strategic decisions for the organization.
Scenario Planning: A set of future scenarios is considered and plans are drawn up to meet any eventualities that may arise.
Practical Examples: Study and analyze successful companies and their strategic decisions to get a feel for what works in strategic thinking.
Skill 3: Emotional Intelligence (EQ)
“When dealing with people, remember you are not dealing with creatures of logic, but with creatures of emotion, creatures bristling with prejudice and motivated by pride and vanity.“
― Dale Carnegie, Author and Leadership Skills Expert
Definition and Significance
Emotional Intelligence is the capacity to perceive a person's feelings and those around them and control both with positivity. The leaders with high EQ can do all the relationship-building processes, keep the working atmosphere going positively and handle all interpersonal dynamics.

Developing Emotional Intelligence
Self-awareness: Reflect on feeling and emotions about thoughts and their relationships with behavior.
Empathy: Practice putting yourself in other people's shoes so that you can understand them and guess their feelings.
People Relationships: Develop good interpersonal relationships with your team members.
Skill 4: Decision Making
“You can't make decisions based on fear and the possibility of what might happen.”
― Michelle Obama
Impact of Strong Decision-Making Skills
Effective decision-making plays a critical role in the successful operation of any organization. The ability to assess all options carefully and select choices that benefit both their team and the organization at large is very crucial for a leader.

Techniques to Enhance Decision-Making Skills
Decision Trees: Draw decision trees to diagram the outcome of different choices.
Cost-Benefit Analysis: The process of weighing the pros against the cons of a decision.
Data-Driven Decisions: Base decisions on data and analytics.
Skill 5: Adaptability
“There can be no life without change, and to be afraid of what is different or unfamiliar is to be afraid of life.”
― Theodore Roosevelt
Necessity of Adaptability in Business
In the fast-paced business world, adaptability forms the basis on which everything grows. Leaders have to change and be in a position to adapt externally to keep in pace with business competitors and follow new trends in business.
Strategies to Become More Adaptable
Resilience: Develop resilience by embracing challenges and considering any setbacks as opportunities for further growth.
Open-Mindedness: Open to new ideas and approaches, even if they run contrary to your own.
Embrace Change: Permit innovation and the will to change in your team, enabling it to grow through its cultural shift.

Analyzing How Leadership Skills Impact on Business Performance
Journal Integration of Social Studies and Business Development published an interesting research on “A Case of Pet&Co Company”. The study looks at how leadership skills impact a startup in the pet health industry. The researchers interviewed the company's CEO and team to understand how different leadership skills affect the business.
Key Findings
- The leader had some strong skills:
- Good at managing emotions
- Communicates tasks clearly
- Listens to team members
- Solves problems collaboratively
- Major weaknesses included:
- Lack of long-term vision
- Low self-motivation
- Poor task follow-up
- Limited innovative thinking
While the leader had some good qualities, gaps in strategic planning, vision and motivation are holding the company back from reaching its full potential. To grow successfully, the CEO needs to improve these areas, especially by developing a clearer long-term strategy and becoming more motivated.
The study suggests that leadership skills are crucial for a startup's success, especially in a competitive and growing market like pet health products.
Conclusion
Business leadership requires a wide range of skills: from communication to strategic thinking, emotional intelligence, and decision-making. Developing these skills will make you a better leader and enable success for your organization. Begin your journey in leadership skills with the courses available at Lrnly Business Courses. Be it enhancing your communication skills or developing strategic thinking – there's a course for you.
FAQ
Leadership skills are crucial in business because they directly impact an organization's ability to achieve its goals, motivate employees and navigate complex challenges. Effective leaders create a vision, inspire team members, and provide clear direction that helps companies adapt to changing market conditions and maintain a competitive edge.
Strong leadership drives innovation, builds positive workplace cultures, and enables organizations to make strategic decisions quickly and effectively. Leaders who can communicate well, solve problems, motivate teams, and create a sense of purpose can transform a group of individual workers into a cohesive, high-performing unit that can overcome obstacles and drive business success.
Toxic leadership is marked by manipulative, abusive, and self-serving behaviors that create a destructive workplace environment. These leaders consistently undermine their team's psychological safety, using intimidation, public humiliation, constant criticism, and emotional manipulation to control employees, often leading to high stress, low morale, and significant staff turnover.
Such leaders typically display narcissistic traits, prioritizing their own ego and career advancement over the well-being of their team members. They frequently engage in gaslighting, blame-shifting, and creating divisive dynamics, fostering a culture of fear, distrust, and constant uncertainty that prevents genuine collaboration and organizational growth.
Bad leaders can be identified by several key behaviors. They consistently prioritize personal success over team development, demonstrate poor leadership skills and create an environment of fear and uncertainty where employees feel undervalued and unmotivated.
Red flags include frequent blame-shifting, inability to take responsibility for mistakes, lack of transparency, inconsistent decision-making, and a tendency to micromanage rather than empower team members. These leaders often show little genuine interest in their employees' professional growth, use intimidation tactics, and create a toxic workplace culture that stifles creativity and collaboration.
People might not see you as a leader because of several potential reasons. Leadership requires more than just a desire to lead – it demands consistent demonstration of key qualities like emotional intelligence, clear communication, reliability, and the ability to inspire and support others through both words and actions.
Common barriers to being perceived as a leader include a lack of confidence, poor communication skills, inability to take initiative, resistance to accountability, and failure to show genuine interest in helping others grow. True leadership is earned through consistent behavior that shows you can guide, support, and bring out the best in people around you.
Poor leadership is characterized by managers who prioritize their own interests over their team's needs and organizational goals. Such leaders typically demonstrate a lack of empathy, poor communication, and an inability to inspire or motivate their employees, often creating toxic work environments where team members feel undervalued and unsupported.
These ineffective leaders frequently micromanage their teams, fail to provide clear direction, and struggle with accountability. They may blame others for failures, avoid taking responsibility for mistakes, and create an atmosphere of fear and uncertainty that prevents open dialogue, innovation, and genuine collaboration among team members.
